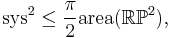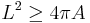Pu's inequality
In differential geometry, Pu's inequality is an inequality proved by Pao Ming Pu for the systole of an arbitrary Riemannian metric on the real projective plane RP2.
Contents |
Statement
A student of Charles Loewner's, P.M. Pu proved in a 1950 thesis (published in 1952) that every metric on the real projective plane 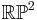 satisfies the optimal inequality
satisfies the optimal inequality
where sys is the systole. The boundary case of equality is attained precisely when the metric is of constant Gaussian curvature.
Reformulation
Alternatively, every metric on the sphere 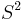 invariant under the antipodal map admits a pair of opposite points
invariant under the antipodal map admits a pair of opposite points 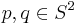 at Riemannian distance
at Riemannian distance 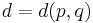 satisfying
satisfying 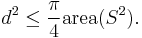
A more detailed explanation of this viewpoint may be found at the page Introduction to systolic geometry.
Filling area conjecture
An alternative formulation of Pu's inequality is the following. Of all possible fillings of the Riemannian circle of length  by a
by a 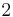 -dimensional disk with the strongly isometric property, the round hemisphere has the least area.
-dimensional disk with the strongly isometric property, the round hemisphere has the least area.
To explain this formulation, we start with the observation that the equatorial circle of the unit 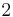 -sphere
-sphere 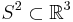 is a Riemannian circle
is a Riemannian circle 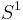 of length
of length 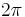 . More precisely, the Riemannian distance function of
. More precisely, the Riemannian distance function of 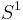 is induced from the ambient Riemannian distance on the sphere. Note that this property is not satisfied by the standard imbedding of the unit circle in the Euclidean plane. Indeed, the Euclidean distance between a pair of opposite points of the circle is only
is induced from the ambient Riemannian distance on the sphere. Note that this property is not satisfied by the standard imbedding of the unit circle in the Euclidean plane. Indeed, the Euclidean distance between a pair of opposite points of the circle is only 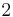 , whereas in the Riemannian circle it is
, whereas in the Riemannian circle it is 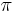 .
.
We consider all fillings of 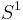 by a
by a 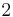 -dimensional disk, such that the metric induced by the inclusion of the circle as the boundary of the disk is the Riemannian metric of a circle of length
-dimensional disk, such that the metric induced by the inclusion of the circle as the boundary of the disk is the Riemannian metric of a circle of length 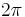 . The inclusion of the circle as the boundary is then called a strongly isometric imbedding of the circle.
. The inclusion of the circle as the boundary is then called a strongly isometric imbedding of the circle.
In 1983 Gromov conjectured that the round hemisphere gives the "best" way of filling the circle even when the filling surface is allowed to have positive genus.
Isoperimetric inequality
Pu's inequality bears a curious resemblance to the classical isoperimetric inequality
for Jordan curves in the plane, where 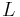 is the length of the curve while
is the length of the curve while  is the area of the region it bounds. Namely, in both cases a 2-dimensional quantity (area) is bounded by (the square of) a 1-dimensional quantity (length). However, the inequality goes in the opposite direction. Thus, Pu's inequality can be thought of as an "opposite" isoperimetric inequality.
is the area of the region it bounds. Namely, in both cases a 2-dimensional quantity (area) is bounded by (the square of) a 1-dimensional quantity (length). However, the inequality goes in the opposite direction. Thus, Pu's inequality can be thought of as an "opposite" isoperimetric inequality.
See also
- Filling area conjecture
- Gromov's systolic inequality for essential manifolds
- Gromov's inequality for complex projective space
- Loewner's torus inequality
- Systolic geometry
- Systoles of surfaces
References
- Gromov, M.: Filling Riemannian manifolds, J. Diff. Geom. 18 (1983), 1–147.
- Gromov, M. Systoles and intersystolic inequalities. (English, French summary) Actes de la Table Ronde de Géométrie Différentielle (Luminy, 1992), 291–362, Sémin. Congr., 1, Soc. Math. France, Paris, 1996.
- Gromov, M. Metric structures for Riemannian and non-Riemannian spaces. Based on the 1981 French original. With appendices by M. Katz, P. Pansu and S. Semmes. Translated from the French by Sean Michael Bates. Progress in Mathematics, 152. Birkhäuser Boston, Inc., Boston, MA, 1999.
- Katz, M. Systolic geometry and topology. With an appendix by J. Solomon. Mathematical Surveys and Monographs, volume 137. American Mathematical Society, 2007.
- Pu, P. M.: Some inequalities in certain nonorientable Riemannian manifolds. Pacific J. Math. 2 (1952), 55–71.
|
|||||||||||